- 11 May 2023
- 3 Minutes to read
- Print
- DarkLight
- PDF
GitLab
- Updated on 11 May 2023
- 3 Minutes to read
- Print
- DarkLight
- PDF
A tool that provides a Git repository manager providing wiki, issue-tracking and continuous integration, and deployment pipeline features
AlertOps and GitLab
GitLab is a web-based DevOps lifecycle tool that provides a Git repository manager providing wiki, issue-tracking and continuous integration, and deployment pipeline features, using an open-source license, developed by GitLab Inc.
AlertOps’ alert management system can be integrated with GitLab to receive and respond to all (predefined status mappings) alerts through email, SMS, push notification or phone alerts. AlertOps would ensure that the alert/job status would reach the appropriate team by using proper workflows, escalation policies and schedules. Based on your ruleset, incidents can be automatically opened and closed, depending on what event GitLab triggers
The above scenario and scope for integration is since AlertOps has a very flexible and simple API/Webhook configuration feature that can be leveraged with GitLab's event notification capabilities.
AlertOps - Inbound Integration
We can define some rulesets in AlertOps so that GitLab can send out events to the AlertOps platform. AlertOps would ensure based on these notifications received, that it would always reach out and assign to the correct person/team by utilizing its escalation policies, schedules, and workflow features.
AlertOps provides Inbound Integrations to integrate with numerous monitoring, chat and ITSM tools. You can configure an inbound integration for GitLab events. (This integration mapping would be defined for "issue" triggers. You can specify mapping as and how you would want to owe to AlertOps' plug-and-play configuration)
At a high level this is how the flow looks like, you define an API integration in the AlertOps platform by defining settings like Integration Name, Escalation rules, recipient users/groups. Once an integration is defined, a unique API URL is generated. This acts as webhook or the gateway through which notifications from GitLab reach AlertOps and thus an incident/alert is created correspondingly. The API can be defined with various settings like URL mappings, filters, escalations etc. as required. GitLab must be defined with a webhook trigger. 
Configure Inbound Integration in AlertOps
- Navigate to Configuration àIntegrations àAdd API Integration à API Integration Detail page
- Select GitLab
- Specify basic settings like the integration name, escalation policy, names of the recipients/groups for which the alerts must be assigned to.
- Click Submit, the API Integration will be created, anda unique URL is provided which acts as the access point and needs to be configured at the source (in this case GitLab), to send events. You can find the integration you just created, and you can give advanced settings and define various configurations for the alerts to be received and processed. For example, you can define when to open and close alerts based on the payload obtained from the API call, filters etc.
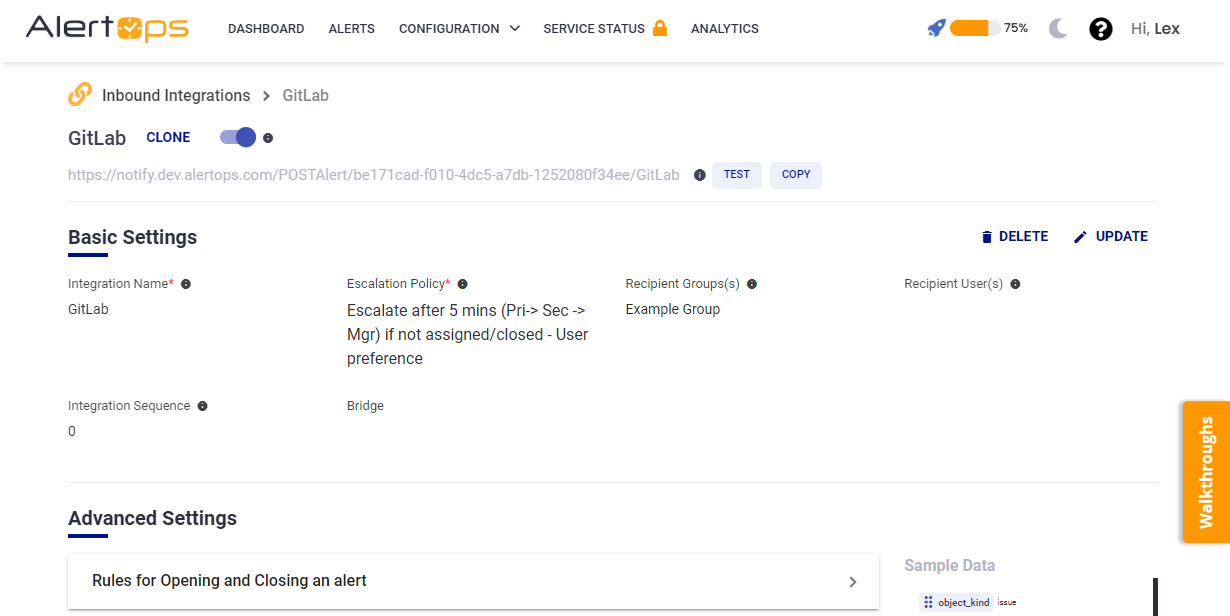
Make a note of the API URL, which will be used in GitLab, so it calls a HTTP POST request to this URL with the body in JSON format containing the alert specific information. AlertOps automatically creates an alert when the status variable (object_attributes^action) contains 'open' or 'reopen'. The incident will also be closed automatically when the status 'close' is received from GitLab. (and updated when 'update' is received).png)
You can similarly define URL mappings as you want, owing to the flexibility provided by AlertOps’ OpenAPI/Plug-and-Play integrations. You can provide other filters and match with regex expressions as well. You can also test the generated URL with sample data.
Configure Integration in GitLab
- Navigate to the project for which the webhook triggers to be created
- In the navigation pane, under 'Settings', select 'Webhooks'
- Give the URL as the AlertOps inbound integration API URL.
- For triggers select the following - Push Events, Issue Events, Confidential Issue Events, Job Events, Pipeline Events, Deployment Events.
- Ideally you can select any event that you would want - you would have to send a test event to AlertOps, see the payload sent out, and do the URL mapping in AlertOps accordingly.
- Add the Webhook. You can also test it
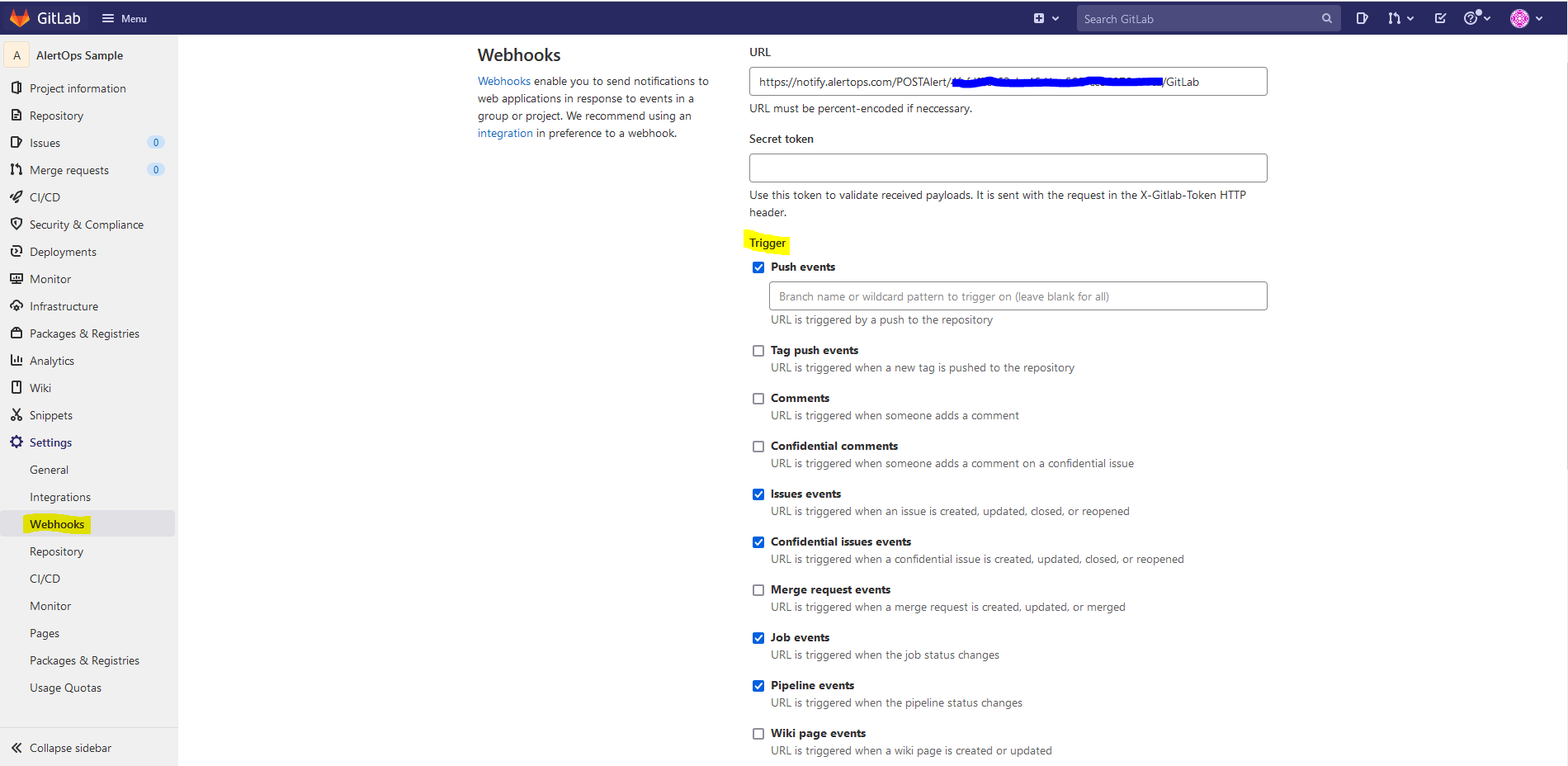
Thats it! You have configured a webhook for different triggers in a GitLab project. Any trigger event would now send an alert to AlertOps for incident management.
Message logs, alert specific information can be viewed in the “Inbound Log” section in AlertOps Dashboard. Alerts can be viewed in the ‘Alerts’ tab as well.
Alert Triggering Information
AlertOps will automatically create an incident when a new alert is received from GitLab when the object_attributes^action field contains "open" or "reopen". (this is for GitLab issues)
If an alert with status "open" or "reopen" matches an existing Open Alert, AlertOps will recognize the new alert as a duplicate and ignore the alert.
The alert will be recorded in the Inbound Messages table as “Mapped Appended.”
AlertOps will automatically close the same incident when an alert with object_attributes^action contains 'close'.


